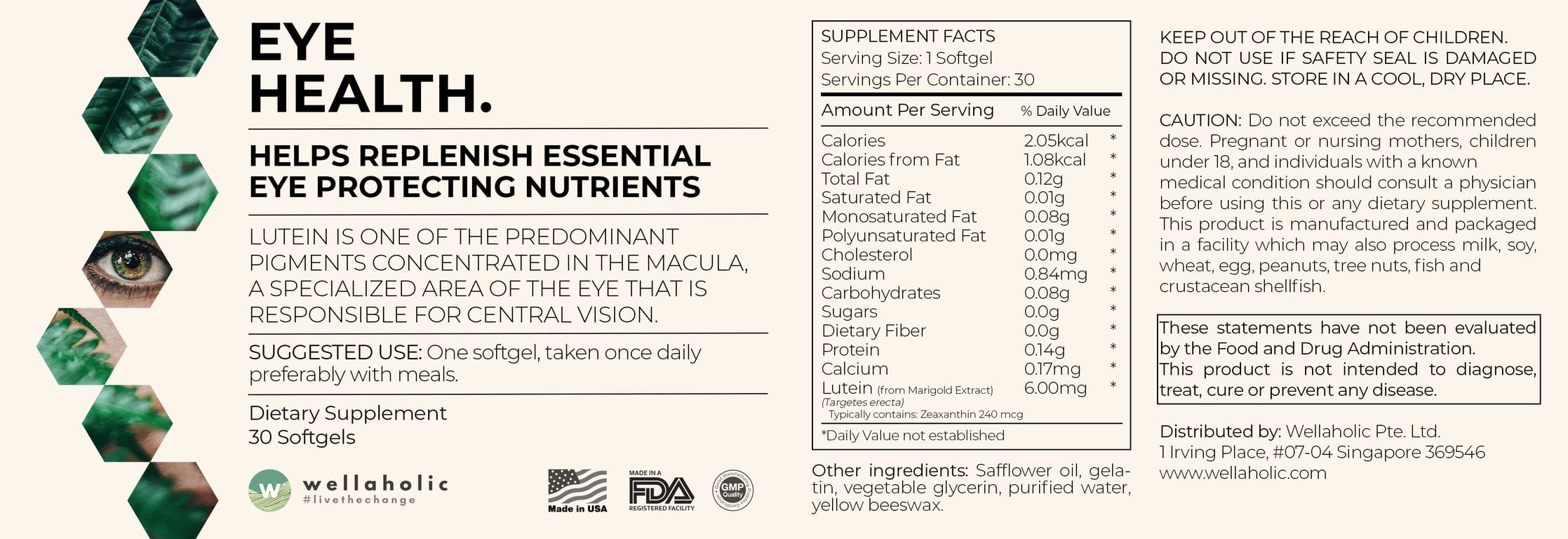
EYE HEALTH
 LUTEIN IS ONE OF THE PREDOMINANT PIGMENTS CONCENTRATED IN THE MACULA, A SPECIALIZED AREA OF THE EYE THAT IS RESPONSIBLE FOR CENTRAL VISION.
LUTEIN IS ONE OF THE PREDOMINANT PIGMENTS CONCENTRATED IN THE MACULA, A SPECIALIZED AREA OF THE EYE THAT IS RESPONSIBLE FOR CENTRAL VISION.
Lutein is called a carotenoid vitamin. It is related to beta-carotene and vitamin A. Foods rich in lutein include broccoli, spinach, kale, corn, orange pepper, kiwi fruit, grapes, orange juice, zucchini, and squash. Lutein is absorbed best when it is taken with a high-fat meal. Many people think of lutein as “the eye vitamin.” They use it to prevent eye diseases including age-related macular degeneration (AMD), cataracts, and retinitis pigmentosa.
Lutein is believed to work as an antioxidant in the eyes, helping to protect the cells from damage caused by free radicals. It is also thought to help filter harmful blue light and reduce inflammation in the eyes, which can contribute to AMD and other eye diseases.
In addition to its potential benefits for eye health, lutein is also believed to have anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties. Some studies have suggested that lutein may help reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, including breast and lung cancer.
Lutein is available in supplement form, but it is always best to try to get nutrients from whole foods whenever possible. Eating a diet rich in fruits and vegetables, particularly those high in lutein, can help support overall health and may provide additional benefits for eye health. If you are considering adding a lutein supplement to your routine, it is important to talk to your healthcare provider first to determine if it is right for you and to discuss the appropriate dosage.
Suggested Use: One Softgel taken once daily preferably



 LUTEIN IS ONE OF THE PREDOMINANT PIGMENTS CONCENTRATED IN THE MACULA, A SPECIALIZED AREA OF THE EYE THAT IS RESPONSIBLE FOR CENTRAL VISION.
LUTEIN IS ONE OF THE PREDOMINANT PIGMENTS CONCENTRATED IN THE MACULA, A SPECIALIZED AREA OF THE EYE THAT IS RESPONSIBLE FOR CENTRAL VISION.